
Disk prolapse
- Home
- Disk prolapse
A disc becomes prolapsed when the soft, jelly-like material that comprises the center of the disc pushes through the fibrous shell and into the spinal column. This condition often leads to neck or back pain when the prolapsed disc comes into contact with a nerve or other soft tissue.
Nerve compression from a prolapsed disc can cause a variety of symptoms, depending on the pathology and location of the problem. Some common forms of radiculopathy (A disease of the root of a nerve, such as from a pinched nerve or a tumour.)
include:
Disk herniation is most often the result of a gradual, aging-related wear and tear called disk degeneration. As you age, your spinal disks lose some of their water content. That makes them less flexible and more prone to tearing or rupturing with even a minor strain or twist.
Most people can’t pinpoint the exact cause of their herniated disk. Sometimes, using your back muscles instead of your leg and thigh muscles to lift large, heavy objects can lead to a herniated disk, as can twisting and turning while lifting. Rarely, a traumatic event such as a fall or a blow to the back can cause a herniated disk
Imaging tests
Nerve tests
Electromyograms and nerve conduction studies measure how well electrical impulses are moving along nerve tissue. This can help pinpoint the location of the nerve damage.
Non-Surgical Herniated Disc Treatments
When no improvement is noted after a course of conservative treatment, surgery might be considered.
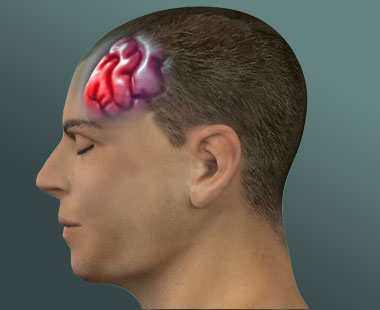
What is head injury?A traumatic brain injury, also referred to an acquired brain injury, occurs when someone suffers a sudden…
read more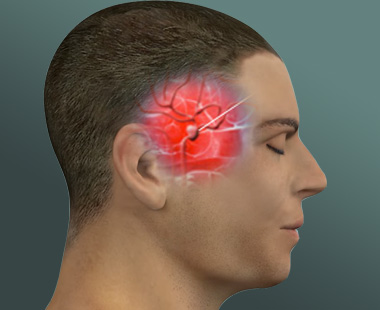
What is Brain Aneurysm?Brain aneurysm is an abnormal bulge in the brain's blood vessel. When it leaks or ruptures, it…
read more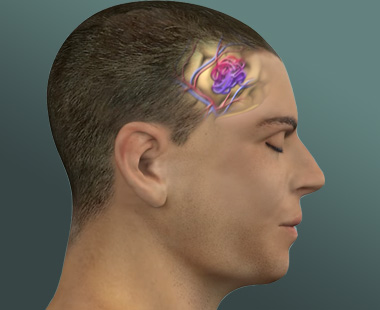
What is a brain arteriovenous malformation ?Normally, arteries carry blood containing oxygen from the heart to the brain, and veins…
read more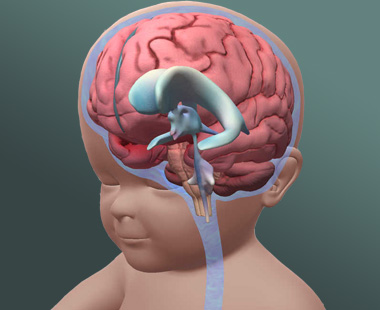
What is Hydrocephalus?Hydrocephalus is commonly referred to as "water on the brain." The so-called "water" is actually cerebrospinal fluid (CSF),…
read more